Emissions from new diesel engines used in generator sets have been regulated by the Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India [G.S.R. 371 (E), 17 May 2002]. The regulations impose type approval certification, production conformity testing and labeling requirements. Certification agencies include the Automotive Research Association of India and the Vehicle Research and Development Establishment. The emission standards are listed below. Engines are tested over the 5-mode ISO 8178 D2 test cycle. Smoke opacity is measured at full load. Concentrations are corrected to dry exhaust conditions with 15% residual O2.
Emission Standards for Diesel Engines ≤ 800 kW for Generator SetsEngine Power (P) Date CO HC NOx PM Smoke g/kWh 1/m P ≤ 19 kW 2004.01 5.0 1.3 9.2 0.6 0.7 2005.07 3.5 1.3 9.2 0.3 0.7 19 kW <> 2004.01 5.0 1.3 9.2 0.5 0.7 2004.07 3.5 1.3 9.2 0.3 0.7 50 kW <> 2004.01 3.5 1.3 9.2 0.3 0.7 176 kW <> 2004.11 3.5 1.3 9.2 0.3 0.7
Emission Limits for Diesel Engines > 800 kW for Generator SetsDate CO NMHC NOx PM mg/Nm3 mg/Nm3 ppm(v) mg/Nm3 Until 2003.06 150 150 1100 75 2003.07 - 2005.06 150 100 970 75 2005.07 150 100 710 75
Emission Standards in India - Generator Sets
Posted by Thilagamani | 3:09 AM | Emission Standard - Genset | 0 comments »A genset, or distributed generator system, is an Electrical generator such as a solar panel, gasoline powered generator, or windmill located in proximity to the end-user rather than in a central location such as those utilized by commercial power providers.
It is best if you read The Magnetism first. Some irons, when dug up, attract other metals. They are called MAGNETS. The reason that they are magnetic is that their DOMAINS are aligned. A rule of magnetism is that LIKE POLES REPEL, UNLIKE POLES ATTRACT. A magnet is surrounded by an invisible MAGNETIC FIELD made of magnetic LINES OF FORCE. Lines of force pass through all materials including insulators. They pass through some more easily than others. These are said to have a lower RELUCTANCE. Iron has a lower reluctance than air. PERMANENT magnets are made of steel or steel alloys. Brass, copper and aluminum do not magnetize. When a piece of wire is moved through a magnetic field, a voltage and current is induced in the wire. The same effect is obtained if the wire is stationary and the field is moved. The direction of current flow is determined by the direction of the field, and the direction of the movement. The amplitude of the voltage is determined by the rate at which the wire cuts the lines of force. This principle is used in the electric generator, where a coil is rotated in a magnetic field to generate electricity. It is also used in the moving coil microphone, where sound causes a coil to vibrate in a magnetic field, generating voltages which represent the sound waves. The Electric Motor Principle is related. It relies on passing a current through a wire in a magnetic field to provide movement. In 1820, Danish physicist Hans Christian Oersted (1777–1851) discovered that an electric current created a magnetic field around it. French physicist André Marie Amperè (1775–1836) then found that a coil of wire with current running through it behaved just like a magnet. In about 1831, English physicist Michael Faraday (1791–1867) discovered the scientific principle on which generators operate: electromagnetic induction. By reversing the work of Oersted and extending the work of Amperè, Faraday reasoned that if a current running through a coiled wire could produce a magnetic field, then a magnetic field could induce (generate) a current of electricity in a coil of wire. By moving a magnet back and forth in or near a coil of wire, he created an electrical current without any other source of voltage feeding the wire.
North attracts South and repels North etc.
The North pointer on a compass is actually a South pole since it is attracted by the North pole of the earth.
These lines of force can be made visible by covering a magnet with a sheet of paper and sprinkling iron filings on the paper.
The lines of force prefer to pass through lower reluctance materials.
Increasing the density of the field or increasing the speed of the wire therefore increases the voltage.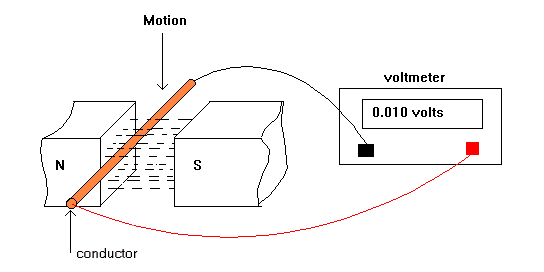
Alternating current (AC):Electric current in which the direction of flow changes back and forth rapidly and at a regular rate. Armature:A part of a generator consisting of an iron core around which is wrapped a wire. Commutator:A slip ring that serves to reverse the direction in which an electrical current flows in a generator. Direct current (DC):Electrical current that always flows in the same direction. Electromagnetic induction:The production of an electromotive force (something that moves electricity) in a closed electrical circuit as a result of a changing magnetic field. Slip ring:The device in a generator that provides a connection between the armature and the external circuit. Faraday also discovered that it makes no difference whether the coil rotates within the magnetic field or the magnetic field rotates around the coil. The important factor is that the wire and the magnetic field are in motion in relation to each other. In general, most AC generators have a stationary (fixed) magnetic field and a rotating coil, while most DC generators have a stationary coil and a rotating magnetic field.
AUXILIARY WINDING
There are two big advantages when a generator is supplied with the aux winding:
1) The voltage is constant during a short circuit: In a generator without the aux winding the AVR is taking power from the main terminals. When you have a short circuit on the main terminals of the generator the AVR is not able to get power from the main terminal. For this reason the AVR doesn’t work and the excitation system is de-powered. The generator switches off and you are not able to recognize that there is a short circuit on the generator terminals. If you want to be sure to recognize that there is a short circuit, the generator should be able to supply during a short circuit, a short circuit current equal at least 3 times the nominal current. You can use electronic devices connected to the AVR (like the Varicomp device in the M8B series) or the aux winding. When you use an electronic device there is always the possibility that the electronic device doesn't work and there is also a little delay before its activation. With the aux winding you don't have these problems: the voltage is simply always the same. With a constant voltage supplied to the AVR you have a short circuit current equal 3 times the nominal current.
2) The voltage is constant during a transient phase: In a generator without the aux winding the AVR is taking power from the main terminals. When you have a load suddenly applied to the generator the voltage of the generator decreases to a value typically equal to 80 - 90% of the nominal value (depending on the value of this load). This voltage drop depends only on the electromagnetic characteristics of the generator and doesn't depend on the way to supply power to the AVR (from the main terminals or from the aux winding). But a generator with the aux winding is better after the first phase when the voltage is less than the nominal value, the voltage that the AVR is taking from the aux winding is equal to the nominal value, also if in the main terminals there is a reduced value. On a generator without aux winding, the AVR is taking a voltage that is less than the nominal value! For this reason in the generator without aux winding just when the AVR needs more power because it has to increase the voltage to the nominal value, it is taking less power because the voltage is less than the nominal value. On a generator with aux winding the voltage is equal to the nominal value also in this situation so the AVR can work better than without aux winding. For this reason the transient behavior of a generator with aux winding is better because the reaction of the AVR is stronger. In the end, the generator is able to come back to the nominal value of the voltage in a period of time shorter than a generator without aux winding or on the other hand you can apply a bigger load with the same period of time of reduced voltage.
Generator Circuit.
The AC generator is a self-excited, single-bearing, brushless, drip-proof, two pole generator which outputs 120/240 VAC at 60 Hz when driven at 3600 rpm. It consists of an excitation system (including exciter stator, exciter rotor, and main rectifier assembly), and a generator system (including main stator and main rotor).
The main stator provides power for excitation of the exciter field through the AVR (the controlling device governing the level of excitation provided to the exciter field) (Figure 1-9). The AVR responds to a voltage sensing signal derived from the main stator winding. By controlling the low power of the exciter field, control of the high-power requirement of the main field is achieved through the rectified output of the exciter armature.
AVR and Diesel Engine Interface.
The AVR detects engine speed and provides voltage fall off with speed, below a pre-selected speed (Hz). This prevents over-excitation at low engine speeds and softens the effect of load switching to relieve the burden on the engine.




